Irish Notary Public Services in Dublin
Apostille and Legalisation
There are two basic types of document legalization - 'Apostille' seal and consular legalisation (consular Legalization). Choice of the type of legalisation in each case depends on the destination country that is country, to which authorities it will be subsequently submitted.
Attachment of an “Apostille” stamp (sometimes this procedure is also called “simplified legalisation” or “Apostillisation ") is used for sending the document to the counties which have acceded to the Hague Convention of 5 October 1961, abolishing the requirement of consular legalization and deceptive simplified procedure of legalization - attachment of an “Apostille " stamp.
Apostille
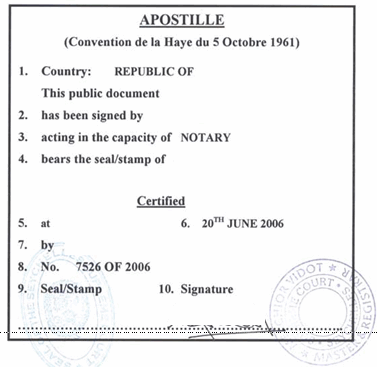 Apostille Notary PublicAn Apostille is a certificate issued by the Department of Foreign Affairs verifying the genuineness of the signature and/or seal of a public officer e.g. a Notary Public, on a public document and the capacity in which he or she has acted. It is sometimes referred to as a 'fast-track' version of legalisation. Legalisation of a document is an implementation of a certain number of formal procedures in order to make the document legal in the territory of another state. The ultimate goal of the document legalization procedure, issued on the territory of one State, is the possibility of submitting it to the authorities of another State.
Apostille Notary PublicAn Apostille is a certificate issued by the Department of Foreign Affairs verifying the genuineness of the signature and/or seal of a public officer e.g. a Notary Public, on a public document and the capacity in which he or she has acted. It is sometimes referred to as a 'fast-track' version of legalisation. Legalisation of a document is an implementation of a certain number of formal procedures in order to make the document legal in the territory of another state. The ultimate goal of the document legalization procedure, issued on the territory of one State, is the possibility of submitting it to the authorities of another State.
Document legalization is almost always required when it is necessary to be submitted to the authorities of another State. This means that a document issued, for example, in Ireland, is legal only on the territory of Ireland, where it can be fully used, but for its submission to the authorities of another country legalization will be required.
The exceptions to this rule are certain types of documents that cannot be legalized, as well as some countries with which Ireland has concluded a bilateral agreement, abolishing the requirement of legalization.
Legalisation of a document is always carried out in the country in which it was issued and / or completed.
The Apostille certificate may be stamped on or attached to the public document required to be apostilled. It is obtained by presenting the document at the Department of Foreign Affairs, Knockmaun House, Passport Office, Lower Mount Street, Dublin 2 and paying the appropriate consular fee.
The Hague Conference has currently 83 Members: 82 States and 1 Regional Economic Integration Organisation. For the dates of membership, please consult the status table of the Statute of the Hague Conference. For an overview of the Membership evolution, click here.
Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade - Apostille
The Apostille procedure applies in lieu of Legalisation between countries that have signed and ratified or acceded to the Hague Convention of 5 October 1961. Ireland ratified the Convention in 1999.
Other countries in which the Apostille procedure applies may be checked on the the Hague Convention website, where a list of countries adhering to the Apostille system abolishing the need for legalisation, and also those countries not Hague Convention Countries Adhering or likely also on the Department of Foreign Affairs webpage.
Legalisation (Legalization)
Legalisation (in some countries spelled 'Legalization') is an internationally recognised procedure for certifying the authenticity of official signatures and/or official seal applied to a public document. It operates by means of an unbroken chain of verifying signatures commencing with that of the first signatory to the document and ending with the signature of the diplomatic or consular representative of the state in which the document is to produced and acted upon.
The legalisation procedure usually commences with the attestation by a Notary Public of the signature of a person to a formal document e.g. a Power of Attorney. The Notary Public having subscribed his or her name and affixed his or her official seal to the document by way of notarial act arranges for the document to be produced to the Registrar of the Supreme Court for the purpose of having the Notary's signature and official seal verified.
The document is then produced at the Consular Section of the Department of Foreign Affairs in Dublin for the purpose of having the signature of the Supreme Court Registrar verified and finally it is produced to the diplomatic or consular representative in Dublin (or London) of the foreign country in which it is intended the document shall be produced for the purpose of having the Irish Consular Officer's signature legalised.
When all the foregoing steps have been completed, the document is said to have been legalised.
Document legalization is not needed in three cases:
- when the institution in which you submit the document does not require its legalisation (legalization);
- when between Ireland and the State, on which territory you plan to use the document, concluded a bilateral agreement, abolishing the requirement of legalization;
- when the legalisation of the document can not be performed by the reason of its kind, type or character.Dublin Notary Public
In all other cases, the legalization of the document for sending it abroad is required.
Other countries in which the Apostille procedure applies may be checked on the the Hague Convention website, where a list of countries adhering to the Apostille system abolishing the need for legalisation, and also those countries not Hague Convention Countries adhereing likely also on the Department of Foreign Affairs webpage.
To summarise, the 1961 Hague Convention abolished the requirement for Foreign Public Documents (e.g. birth, death and marriage certificates, documents issued by a Notary Public) to be legalised for countries that are parties to the Convention.
The Convention entered into force for Ireland on 9 March 1999. For further information on the Hague Convention please access their website.
However, countries that are parties to the Convention may request the bearer of a document issued by a public authority to obtain an Apostille from the Authorities of the country that issued the document.
An Apostille involves the addition of a certificate, either stamped on the document itself or attached to it. It certifies the country of origin of the document, the identity and capacity in which the document has been signed and the name of any authority which has affixed a seal or stamp to the document.
Documents that the Dept of Foreign Affairs can Authenticate\Apostille
The Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade can Authenticate\Apostille documents of Irish origin provided that they bear an original signature, seal or stamp from an Irish practising public official or organisation. An Irish document means that it originated or has been executed in Ireland. If a practising Irish solicitor, Notary Public or Commissioner for Oaths is signing a document they should state clearly what exactly it is they are certifying in relation to the document. They must sign their own name and not use a company signature.
Examples of Documents the Department can Authenticate\Apostille are:
The Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade can Authenticate\Apostille public documents which have been executed in the territory of One Contracting State and which have to be produced in the territory of another Contracting State.
Examples:
- Original certificates issued by the General Registers Office (GRO)
- Company documents issued by the Companies Registration Office
- Documents signed by the Chambers of Commerce in Ireland
- Court documents, Powers of Attorney, and other Notarial Acts can be Authenticated provided they bear an original signature, seal or stamp from a practising Irish solicitor\ Notary Public in Ireland
- Educational Certificates can be Authenticated provided they fall within the National Framework of Qualifications established by the National Qualifications Authority of Ireland \ are recognised by the Department of Education.
- We can also Authenticate\Apostille medical reports signed by a doctor who is registered with the Medical Council of Ireland.
- Garda Clearance letters confirming a person's details for Consular purposes must be issued from the Superintendent's Office of the Garda station where you last resided in Ireland. This letter must bear an original stamp and signature of the Garda Siochána.
- An appointment is necessary for large numbers of documents and for full foreign adoption dossiers.
- Photocopies of Documents: The Department can Authenticate\Apostille photocopies of certain types of documents provided they have been certified by a practising Irish Solicitor or Notary Public in Ireland. However, you should in the first instance confirm with the authority to whom you are presenting the document that a certified copy will be acceptable to them.
The ABCs of Apostilles
L'ABC de l'Apostille
Brochure à l'attention des utilisateurs d'Apostilles, qui fournit des réponses courtes aux questions les plus fréquemment posées, notamment quand, où etcomment les Apostilles sont émises et quels sont leurs effets.
Téléchargez ici.
How to get your Document Authenticated\Apostilled
Documents that have been executed in Ireland, and which are to be Authenticated or Apostilled by the Department can be:
 Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade - Apostille ServicePresented to the Department at its Public Office at the following address:
Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade - Apostille ServicePresented to the Department at its Public Office at the following address:
Consular Section
Department of Foreign Affairs and TradeKnockmaun House, Passport Office, Lower Mount Street, Dublin 2
or sent via post to:
Consular Section
Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade
Knockmaun House, Passport Office, Lower Mount Street, Dublin 2
Documents sent by post must include the following:
A brief covering letter stating your name, return address, telephone number, you must state what country the document(s) are for use in, and you must include the appropriate fee.
Tel. (01) 408 2174
(01) 408 2322
(01) 408 2557
(01) 408 2576
For the Munster area:
Consular Services,
Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade,
1A South Mall,
Cork
Tel : 021 4944765 / 021 4944766
Opening Hours:
The opening hours for the Public Offices in Dublin and Cork are as follows:
Monday - Friday (excluding Bank Holidays)
0930 - 1300
1430 - 1600
Fees Charged by the Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade
A fee of €40 is charged for each Apostille or Authentication. There is a standard fee of €100 for a series of Apostilles or Authentications in relation to inter-country adoptions. All Post Placement Reports have a fee of €40.00
Please note that there may be an additional administration fee if applying for these services from our offices abroad. Fees will be notified on request.
Methods of Payment
This section relates to services available at the Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade in Dublin and Cork.
Payment can be made by Cash, Bank Draft (made payable to the 'Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade'), Irish Postal Order or by Credit/Debit card.
It should be noted that all bank drafts must be drawn on an Irish bank or a bank showing a connection with a bank in Ireland. Personal cheques are no longer accepted.
_____________________________________________________________
E-Register Verification of Apostilles and Authentications
The online electronic register enables you to verify the authenticity of an Apostille or Authentication issued by the Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade in Ireland from 01 January 2013.
In order to verify an Apostille or Authentication, please click here
_____________________________________________________________
Legalisation
Irish Diplomatic and Consular Missions abroad can legalise documents executed abroad for use in Ireland.
Administering oaths, affirmations and statutory declarations and certifying copies of documents:
Irish Diplomatic and Consular Officers abroad are empowered under Irish law to administer oaths, affirmations and statutory declarations. They can also certify copies of original Irish documents or translations.
If you require any of these services, contact your nearest Irish Diplomatic or Consular Mission.
The fee for these services in local currency and methods of payment will be notified, on request, by the relevant Mission.
Contact us for more information about our services. Our experienced consultant will treat each individual situation with due attention and provide you with an excellent service. Our notary service office is open from 9 am to 5.30 pm on business days.
Telephone: 353-1-6712773
CONVENTION ABOLISHING THE REQUIREMENT OF LEGALISATION FOR FOREIGN PUBLIC DOCUMENTS
amaica accedes to the Apostille Convention
On 2 November 2020, Jamaica deposited its instrument of accession to the HCCH Convention of 5 October 1961 Abolishing the Requirement of Legalisation for Foreign Public Documents (Apostille Convention).
With the accession of Jamaica, the Apostille Convention now has 119 Contracting Parties. It will enter into force for Jamaica on 3 July 2021. More information on this Convention is available on the Apostille Section of the HCCH website.
Although not yet a Member of the HCCH, Jamaica is now a Contracting Party to two HCCH Conventions.
Listed below are the countries that are participants of the Apostille Convention (Hague Treaty Convention 12) and the convention is in force with the United States of America. The official list can be found at The Hague Conference on Private International Law’s website:
http://hcch.e-vision.nl/index_en.php?act=conventions.status&cid=41
|
|
|
E-mail: cy@yor.ie
*An addiontal fee is payable for a same day service to the Department of Foreign Affairs & Trade to have an Apostille affixed to any documents
